How to Work Eco Water
Galvanic treatment of water
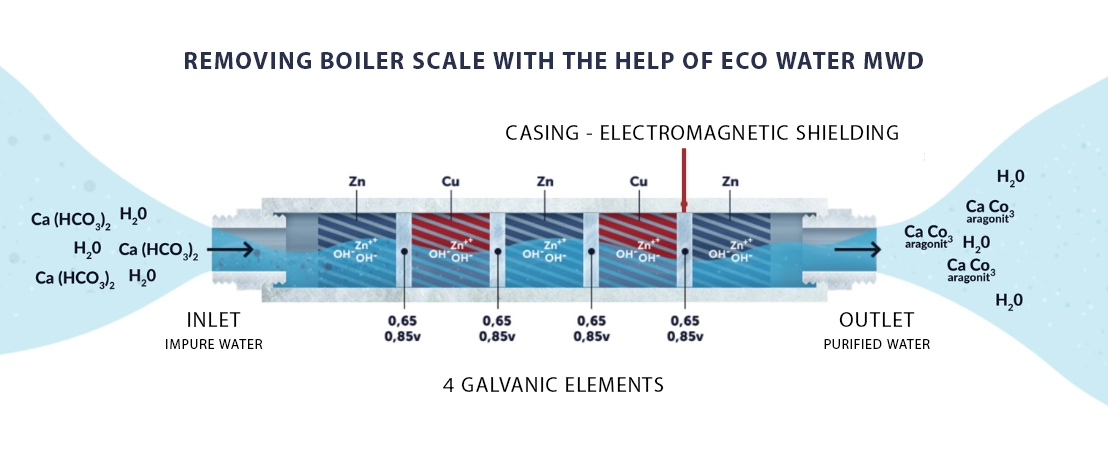
For the proper naming of the technology used, it would be better to use the term physical or electrolytic water treatment. This means that the electrochemical reactions that occur as a result of the interaction between the cathode and anode, immersed in the electrolyte, change the structure of the minerals contained in the water. The elimination of the formation of limescale, mainly Ca and Mg, is of interest to people from the point of view of energy saving and extending the life of water supply systems and water-consuming devices while preserving all the healthy properties of drinking water.
Mode of operation
At the same time, free zinc ions are released into the water from the titanium-zinc anode. Calcium (Ca2+), which is dissolved in the water and is the main cause of scale formation in pipelines and heat exchangers, is present in the water in the form of calcium bicarbonate Ca(HCO3)2.
Under the influence of the hydrodynamics of water and the change in water temperature, calcium bicarbonate breaks down into carbon dioxide and the poorly soluble calcium carbonate (calcite). The released carbon dioxide CO2 combines with zinc cations, forming zinc carbonate ZnCO3. Calcite CaCO3, which crystallizes in a trigonal system, gives rise to aragonite (a polymorphic form of CaCO3), which crystallizes in a rhombohedral system. Aragonite has the property of being washed away under the influence of the water system.
This only happens when the galvanic water purification product is manufactured correctly. Our product, Eco Water MWD, meets these conditions. Aragonite, when passing through the pipeline, also has an abrasive effect on the existing limescale in the pipes formed during the passage of the water flow. The free zinc anions tend to bind with already formed calcium cations and thus wash away calcium deposits and calcium compounds from the water supply system.
Another positive effect is the transformation of the upper oxidized layers of the metal through the limiting reactions of zinc. The existing layers of boiler scale and rust are constantly being destroyed in microscopic quantities and are flushed out of the pipes with the water flow. After the removal of the boiler scale, a protective anti-corrosion layer gradually forms on the surface of the pipe - magnetite, which stops further corrosion of the system.
Longevity and operation
The longevity of the Eco Water MWD device is determined by the hardness of the water, the influence of the concentration of CO2 in the water, and the pH of the water. With a significant increase in water hardness and water acidity below 6.5, the zinc anode deteriorates faster, which reduces the lifespan of the device.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the Eco Water device suitable for cooking equipment?
Does the use of Eco Water affect the functioning of home wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs)?
How does Eco Water actually work? When can the difference in water qualities be detected?
If I install Eco Water on the main water supply pipe, what will happen to limescale? Won't the water supply system get clogged with limescale? And what will happen to the electric kettle, coffee maker, and water heater?
How would your device help when using a pool?